






Thank you for actually answering the question with a source, rather then hearsay or conjecture without sources.
To answer from a quote:
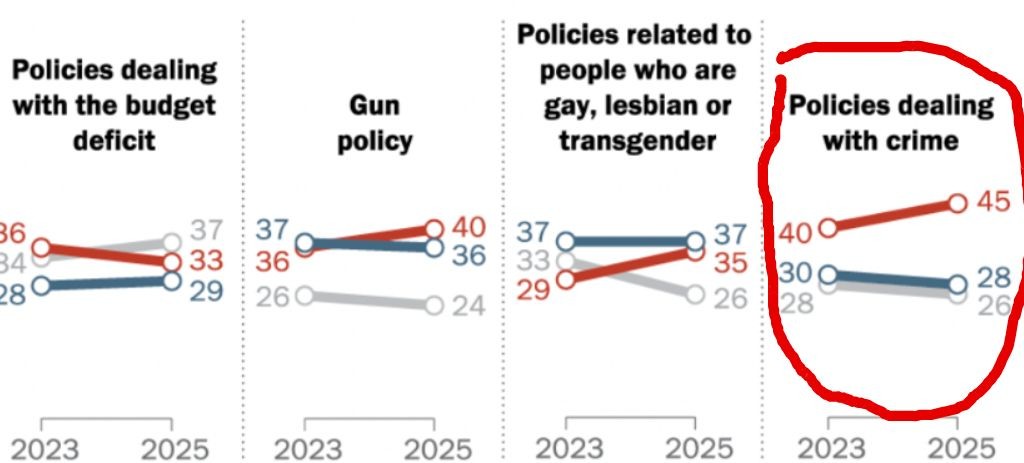
Examining trends over a longer timeframe, violent crimes are below levels seen in the first half of 2019, the year prior to the onset of the COVID pandemic and racial justice protests of 2020. There were 14% fewer homicides in the study cities in the first half of 2025 than in the first half of 2019. Similarly, reported aggravated assault (-5%), gun assaults (-4%), sexual assault (-28%), domestic violence (-8%), robbery (-30%), and carjacking (-3%) were lower in 2025


I would say they offer an answer where google may not as well, given the lower attention threshold people.
This is also a combination of years of SEO attempting to manipulate rankings, and the web becoming more diverse and complicated. Which makes finding answer more complicated, but in general I would agree that Google’s algorithm has gotten worse and been drawn more to making money.


Beyond my frustration at this being buried in a video podcast, I also would rather promote why people should be worried about privacy in a concrete and direct way.
Year 0: You’re a healthy middle-class person who “has nothing to hide”
Year 3: Your insurance premiums inexplicably rise. You don’t know your fitness tracker data was sold and correlated with your grocery purchases.
Year 5: Passed over for promotion. Algorithm flagged social media posts about work stress as “low resilience indicator.”
Year 7: Attend peaceful protest. Face-recognition adds you to databases. Now randomly selected for “additional screening” at airports.
Year 9: Can’t get affordable loan. Your zip code + purchase history + social network = high risk score. The specific formula is proprietary.
Year 10: Chronic condition develops. Can’t get treatment covered - insurer says it’s “pre-existing” based on data you didn’t know they had from a DNA test you took for fun in Year 2.
Your lifespan: Statistically reduced by 5-10 years compared to privacy-protected cohort.
Privacy isn’t about “having something to hide.” It’s the immune system of human dignity, economic fairness, political freedom, and literally - survival.
Without it, you become a data object to be optimized for others’ profit and control, not a human with agency over your own life.


Ah, you mean https://fightchatcontrol.eu/.
I am not aware of anything yet, apart from what the article suggests. https://digital-markets-act.ec.europa.eu/contact-dma-team_en


Ah yes, American exceptionalism. Silly me. Have to win as an underdog. If only we had education and learning history as part of our American ethos.

Exactly. I am curious how this has changed since BRICS was created, and also how current Cheeto in Chief policies will impact it over time.


I always wonder why people venerate Edison so much. He did innovate, but man was he a shifty barron.


For those in Europe, write your representatives.
Fro me f-droid’s post: https://f-droid.org/2025/09/29/google-developer-registration-decree.html
What do we propose?
Regulatory and competition authorities should look carefully at Google’s proposed activities, and ensure that policies designed to improve security are not abused to consolidate monopoly control. We urge regulators to safeguard the ability of alternative app stores and open-source projects to operate freely, and to protect developers who cannot or will not comply with exclusionary registration schemes and demands for personal information.
If you are a developer or user who values digital freedom, you can help. Write to your Member of Parliament, Congressperson or other representative, sign petitions in defense of sideloading, and contact the European Commission’s Digital Markets Act (DMA) team to express why preserving open distribution matters. By making your voice heard, you help defend not only F-Droid, but the principle that software should remain a commons, accessible and free from unnecessary corporate gatekeeping.
https://f-droid.org/2025/09/04/twif.html [^antifeatures]: F-Droid Anti-Features overview: https://f-droid.org/docs/Anti-Features/ [^howmanyusers]: How many F-Droid users are there, exactly? We don’t know, because we don’t track users or have any registration. “No user accounts, by design”: https://f-droid.org/2022/02/28/no-user-accounts-by-design.html [^sideloading]: ‘“Sideload” is a weird euphemism that the mobile duopoly came up with; it means “installing software without our permission,” which we used to just call “installing software” (because you don’t need a manufacturer’s permission to install software on your computer).’ — Pluralistic: Darth Android: https://pluralistic.net/2025/09/01/fulu/ [^playprotect]: “Google Play Protect checks your apps and devices for harmful behavior”: https://support.google.com/googleplay/answer/2812853


Each myth is contiguous in each episode rather than being interweaved. Much more satisfying.


Just give up and get streamlined mythbusters. Easier to watch anyway.


Once and a while I go to the Movies and often end up asking why I thought it was a good idea to pay exorbitant prices for the 30 mins of mixed ads/previews, all for a cliche plot of yet another reboot. Which inspires me to not go to the movies for another 6 months or year, and just go for a run outside.


Can you say more on your point on local or allied production? I haven’t kept up, but last I heard the domestic US production of chips is many years away and likely to be generations older than Taiwan can produce. I was under the impression that these production lines take many many years to set up and train people for, unlike some manufacturing.


Admittedly Wikipedia, so some verification needed, but telling.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Smoot–Hawley_Tariff_Act
The tariffs initially appeared to be a success; according to historian Robert Sobel, “Factory payrolls, construction contracts, and industrial production all increased sharply.” However, larger economic problems loomed in the guise of weak banks. When the Creditanstalt of Austria failed in 1931, the global deficiencies of the Smoot–Hawley Tariff became apparent.[12]
U.S. imports decreased 66% from $4.4 billion (1929) to $1.5 billion (1933), and exports decreased 61% from $5.4 billion to $2.1 billion. US gross national product fell from $103.1 billion in 1929 to $75.8 billion in 1931 and bottomed out at $55.6 billion in 1933.[21] Imports from Europe decreased from a 1929 high of $1.3 billion, to $390 million in 1932. U.S. exports to Europe decreased from $2.3 billion in 1929 to $784 million in 1932. Overall, world trade decreased by some 66% between 1929 and 1934.[22]
Unemployment was 8% in 1930 when the Smoot–Hawley Act was passed but the new law failed to lower it. The rate jumped to 16% in 1931 and to 25% in 1932–1933.[23] There is some contention about whether this can necessarily be attributed to the tariff.[24][25] The Great Depression was already in motion before Smoot-Hawley, mainly due to financial instability, falling demand, and poor banking practices. However, the tariff worsened the crisis by shrinking global trade, hurting farmers, and reducing employment in export-dependent industries. Had it not passed, the Depression still would have occurred, but perhaps with less severity.


https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Event_data_recorder#NHTSA_ruling
Since there was already an overwhelming trend for voluntary EDR installation, the ruling did not require manufacturers to install EDRs in vehicles produced for North America. Based on its analysis, NHTSA estimated that by 2010, over 85% of vehicles would already have EDRs installed in them, but warned that if the trend did not continue, the agency would revisit their decision and possibly make installation a requirement.
The mandate did, however, provide a minimum standard for the type of data that EDRs would be required to record, consisting of at least 15 types of crash data, including pre-crash speed, engine throttle, brake use, measured changes in forward velocity (Delta-V), driver safety belt use, airbag warning lamp status and airbag deployment times.
In addition to the required data, NHTSA also set standards for 30 other types of data to be recorded if EDRs were voluntarily configured. For example, if a manufacturer configured an EDR to record engine RPMs or ABS activity, then the EDR would have to record 5 seconds of those pre-crash data in half-second increments.
…


Especially a utility of all things.